NICE DCV¶
Install NICE DCV (user-computer)
Install VPN client VPN Access
How to Use¶
Read the documentation on VNC server.
Run VNC
- Login to Barbora
[username@yourPC]$ ssh -i path/to/your_id_rsa user@login1.Barbora.it4i.cz
- Run a Job on Barbora on the Vizserv1 (or Vizserv2)
[user@login1]$ salloc -p qviz -A OPEN-XX-XX --nodes=1 --ntasks=4 --time=04:00:00 --nodelist=vizserv1 --job-name=Vizserver1
You are connected to Vizserv1 now.
[yourusername@vizserv1 ~]$
VNC Server
- Create a VNC Server Password
Note
A VNC server password should be set before the first login to VNC server. Use a strong password.
[yourusername@vizserv1 ~]$ vncpasswd
password:
verify:
- Check the display number of the connected users
[yourusername@vizserv1 ~]$ ps aux | grep Xvnc | sed -rn 's/(\s) .*Xvnc.* (\:[0-9]+) .*/\1 \2/p'
username :15
username :61
.....
Note
The VNC server runs on port 59xx, where xx is the display number. To get your port number, simply add 5900 + display number, in our example 5900 + 11 = 5911. Calculate your own port number and use it instead of 5911 from examples below.
- Start your remote VNC server
Note
Choose the display number which is different from other users display number. Also remember that display number should be lower or equal 99.
[yourusername@vizserv1 ~]$ vncserver :11 -geometry 1600x900 -depth 24
Running applications in /etc/vnc/xstartup
VNC Server signature: f0-3d-df-ee-6f-a4-b1-62
Log file is /home/yourusername/.vnc/vizserv1:11.log
New desktop is vizserv1:11 (195.113.250.204:11)
- Check the display number
[yourusername@vizserv1 ~]$ ps aux | grep Xvnc | sed -rn 's/(\s) .*Xvnc.* (\:[0-9]+) .*/\1 \2/p'
username :15
username :61
yourusername :11
.....
Note
You started a new VNC server. The server is listening on port 5911 (5900 + 11 = 5911).
Your VNC server is listening on port 59xx, in our example on port 5911.
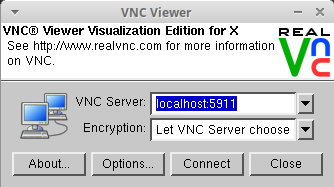
VNC Client (your local machine) You are going to connect your local machine to remote VNC server.
- Create the SSH tunnel (on your local machine) for port 59xx and for the range of ports 7300-7305.
[username@yourPC]$ ssh -i path/to/your_id_rsa -TN -f user@vizserv1.barbora.it4i.cz -L 5911:localhost:5911 -L 7300:localhost:7300 -L 7301:localhost:7301 -L 7302:localhost:7302 -L 7303:localhost:7303 -L 7304:localhost:7304 -L 7305:localhost:7305
To create an SSH tunnel on Windows, download the PuTTY installer and follow the instructions in the VNC server section.
-
Run NICE DCV or one of the recommended clients on your local machine. Recommended clients are TightVNC or TigerVNC (free, open source, available for almost any platform).
-
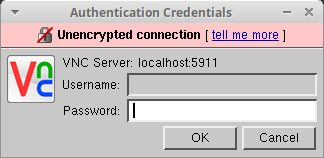
Fill in the localhost:59xx address, click Connect, and enter the password.
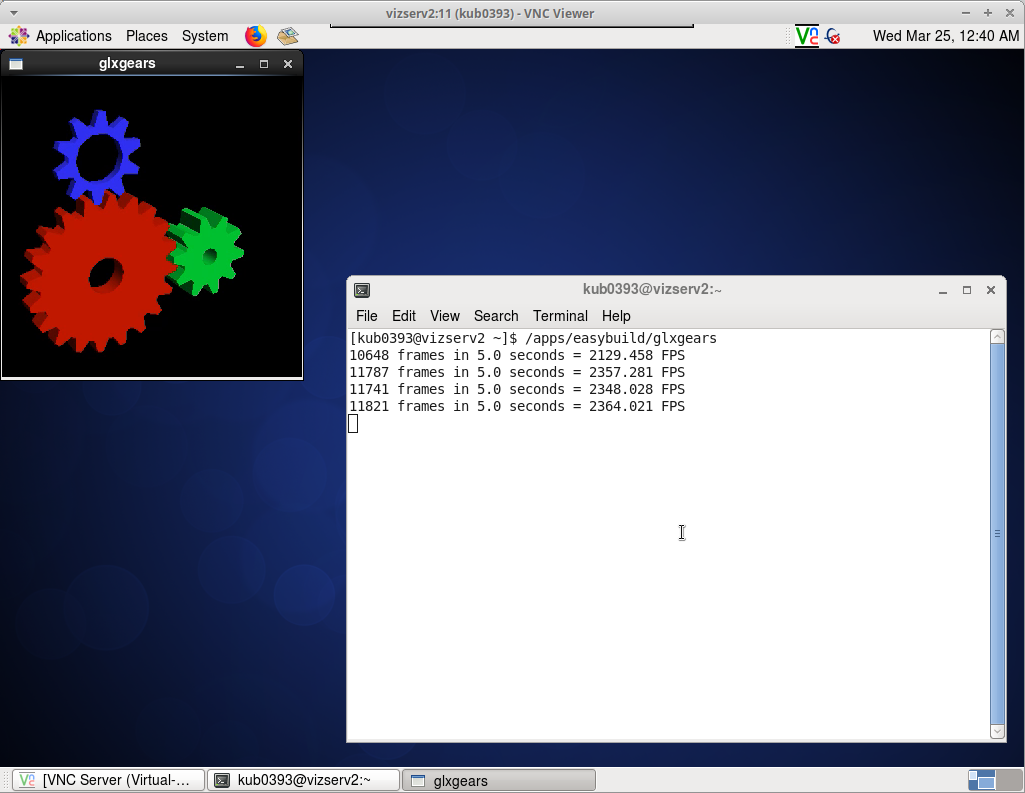
Test the OpenGL functionality on Vizserv
- Run the command in the VNC terminal
[kub0393@vizserv1 ~]$ /apps/easybuild/glxgears
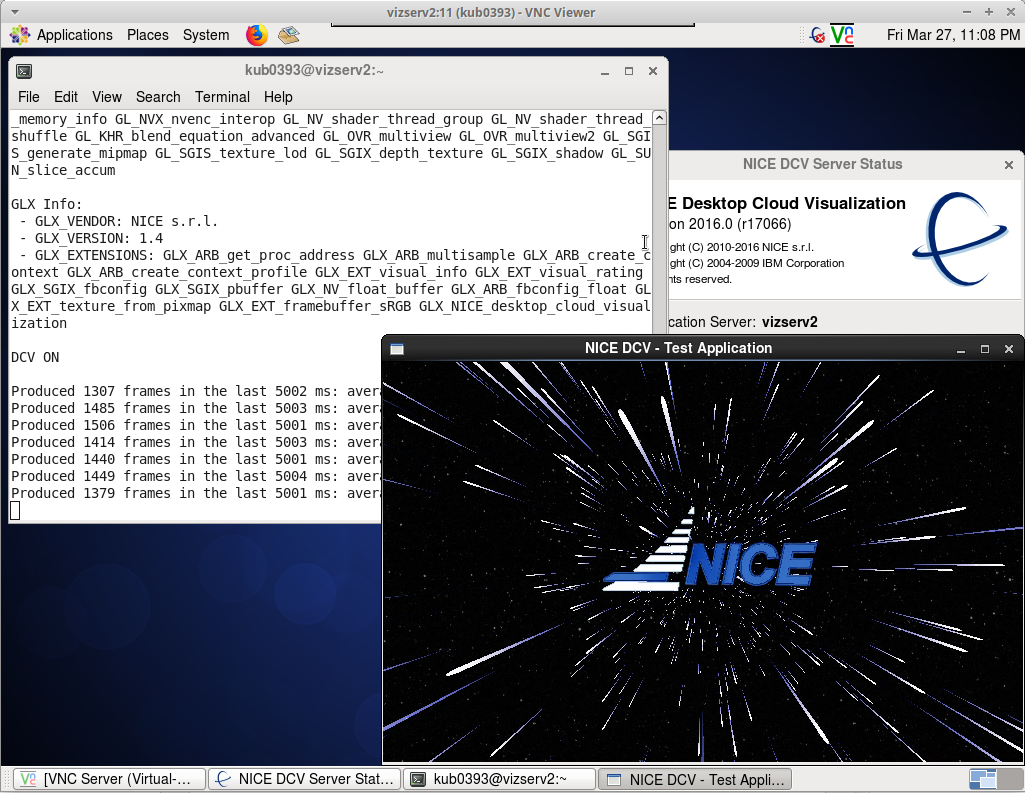
Test the NICE DCV functionality
- Run the command in VNC terminal
[kub0393@vizserv1 ~]$ dcvtest
Stop the Service Correctly After Finishing Work¶
On VNC server site
- Logout from your local VNC window
On your local machine
- Find the Process ID (PID) of your SSH tunel
[username@yourPC]$ netstat -natp | grep 5911
(Not all processes could be identified, non-owned process info
will not be shown, you would have to be root to see it all.)
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:5911 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 5675/ssh
tcp6 0 0 ::1:5911 :::* LISTEN 5675/ssh
or
[username@yourPC]$ lsof -i :5911
COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME
ssh 5675 user 5u IPv6 571419 0t0 TCP ip6-localhost:5911 (LISTEN)
ssh 5675 user 6u IPv4 571420 0t0 TCP localhost:5911 (LISTEN)
Note
PID in our example is 5675. You also need to use the correct port number for both commands above. In this example, the port number is 5911. Your PID and port number may differ.
- Kill the process
[username@yourPC]$ kill 5675
- If on Windows, close Putty.